App Engine Logging
Overview
This documentation provides a detailed walkthrough on how to set up Google App Engine to send the logs directly to SigNoz. By the end of this guide, you will have a setup that automatically sends your App Engine logs to SigNoz.
Here's a quick summary of what we will be doing in this guide
- Create and configure App Engine
- Create Pub/Sub topic
- Create Log Router to route the App Engine logs to SigNoz
- Create Compute Engine instance
- Create OTel Collector to route logs from Pub/Sub topic to SigNoz Cloud
- Invoke the deployed App Engine service to generate logs
- Send and Visualize the logs in SigNoz Cloud
Prerequisites
- Google Cloud account with administrative privilege or App Engine Admin privilege.
- SigNoz Cloud Account (we are using SigNoz Cloud for this demonstration, we will also need ingestion details. To get your Ingestion Key and Ingestion URL, sign-in to your SigNoz Cloud Account and go to Settings >> Ingestion Settings)
- Access to a project in GCP
- Cloud Build API is enabled
Get started with App Engine Configuration
Create the App Engine service using the following steps:
Step 1: Install the Google Cloud CLI.
Step 2: To initialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloud init
Step 3: Run the following gcloud command to enable App Engine and create the associated application resources. Note that the location you select cannot be changed later.
gcloud app create
Step 4: In this example, we will be building the Python 3 application. For this,
- Download the sample application repository using Git:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/python-docs-samples
Alternatively, you can download the sample as a zip file and then extract it.
- Navigate to the directory that contains a copy of the files from the previous step:
cd python-docs-samples/appengine/standard_python3/hello_world
Note that we have app.yaml file located in this folder.
- You can modify the
main.pyfile in this folder usingvi main.pyto include a couple of print statements which will be logged when the service is invoked.
@app.route("/")
def hello():
"""Return a friendly HTTP greeting.
Returns:
A string with the words 'Hello World!'.
"""
print("Starting the hello world app engine application...") # <- new print statement added
return "Hello World!"
- When on this folder which contains
app.yaml, you can deploy your service using the command:
gcloud app deploy
- On running the above command, the service will get deployed on the App Engine, and you will get the logs containing the endpoint which can be used to trigger the deployed service (highlighted in red in the screenshot).
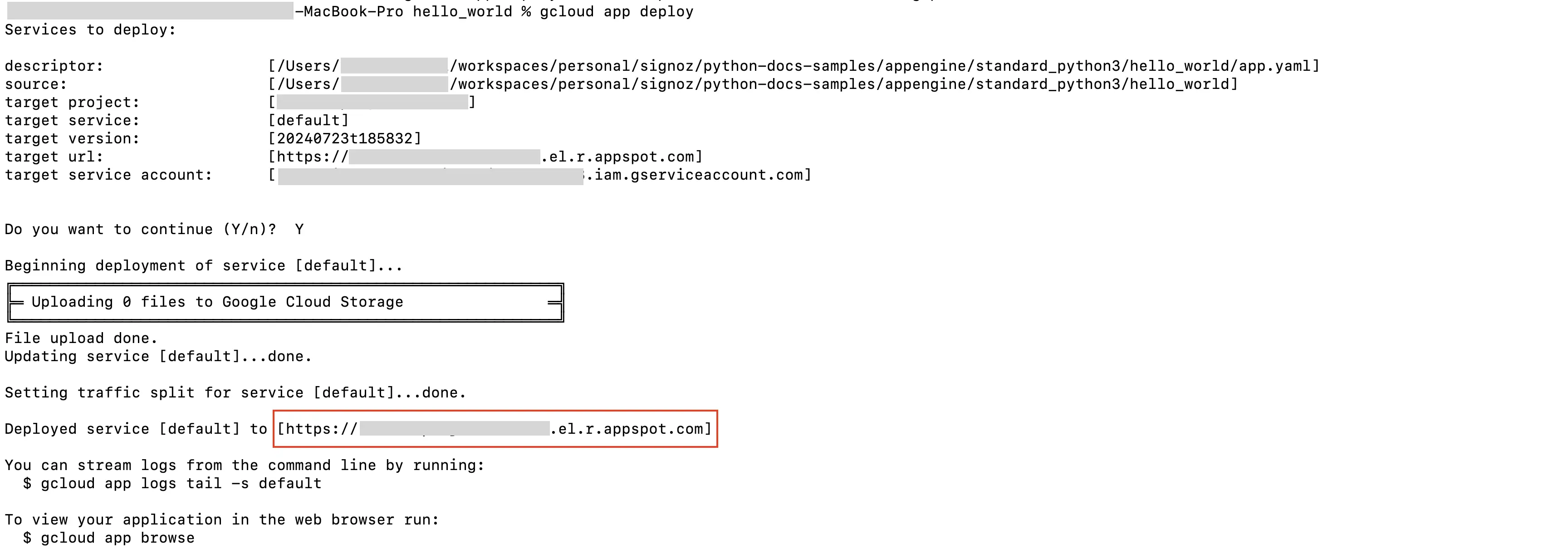
App Engine Deploy Logs
Open the URL in the new browser which will invoke the service and put out the print statements in the logs.
Viewing the logs
- In the GCP console, search for
Logsand go toLogs Explorerservice. - Check for the recent logs or use the
Querytextbox to search for the logs containing the print statements from the service deployed to the App Engine.
Create PubSub Topic
Follow the steps mentioned in the Creating Pub/Sub Topic document to create the Pub/Sub topic.
Create Log Router to Pub/Sub Topic
Follow the steps mentioned in the Log Router Setup document to create the Log Router.
To ensure you filter out only the App Engine logs, use the following filter conditions:
resource.type="gae_app"
Setup OTel Collector
Follow the steps mentioned in the Creating Compute Engine document to create the Compute Engine instance.
Install OTel Collector as agent
Firstly, we will establish the authentication using the following commands:
- Initialize
gcloud:
gcloud init
- Authenticate into GCP:
gcloud auth application-default login
Let us now proceed to the OTel Collector installation:
Step 1: Download otel-collector tar.gz for your architecture
wget https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-collector-releases/releases/download/v0.88.0/otelcol-contrib_0.88.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz
Step 2: Extract otel-collector tar.gz to the otelcol-contrib folder
mkdir otelcol-contrib && tar xvzf otelcol-contrib_0.88.0_linux_amd64.tar.gz -C otelcol-contrib
Step 3: Create config.yaml in the folder otelcol-contrib with the below content in it. Replace <region> with the appropriate SigNoz Cloud region. Replace SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY with what is provided by SigNoz:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
googlecloudpubsub:
project: <gcp-project-id>
subscription: projects/<gcp-project-id>/subscriptions/<pubsub-topic's-subscription>
encoding: raw_text
processors:
batch: {}
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
tls:
insecure: false
headers:
"signoz-ingestion-key": "<SigNoz-Key>"
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
metrics:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
logs:
receivers: [otlp, googlecloudpubsub]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
Step 4: Once we are done with the above configurations, we can now run the collector service with the following command:
From the otelcol-contrib, run the following command:
./otelcol-contrib --config ./config.yaml
Run in background
If you want to run OTel Collector process in the background:
./otelcol-contrib --config ./config.yaml &> otelcol-output.log & echo "$!" > otel-pid
The above command sends the output of the otel-collector to otelcol-output.log file and prints the process id of the background running OTel Collector process to the otel-pid file.
If you want to see the output of the logs you’ve just set up for the background process, you may look it up with:
tail -f -n 50 otelcol-output.log
You can now trigger the App Engine service URL a few times, and see the logs from the App Engine on SigNoz Cloud.
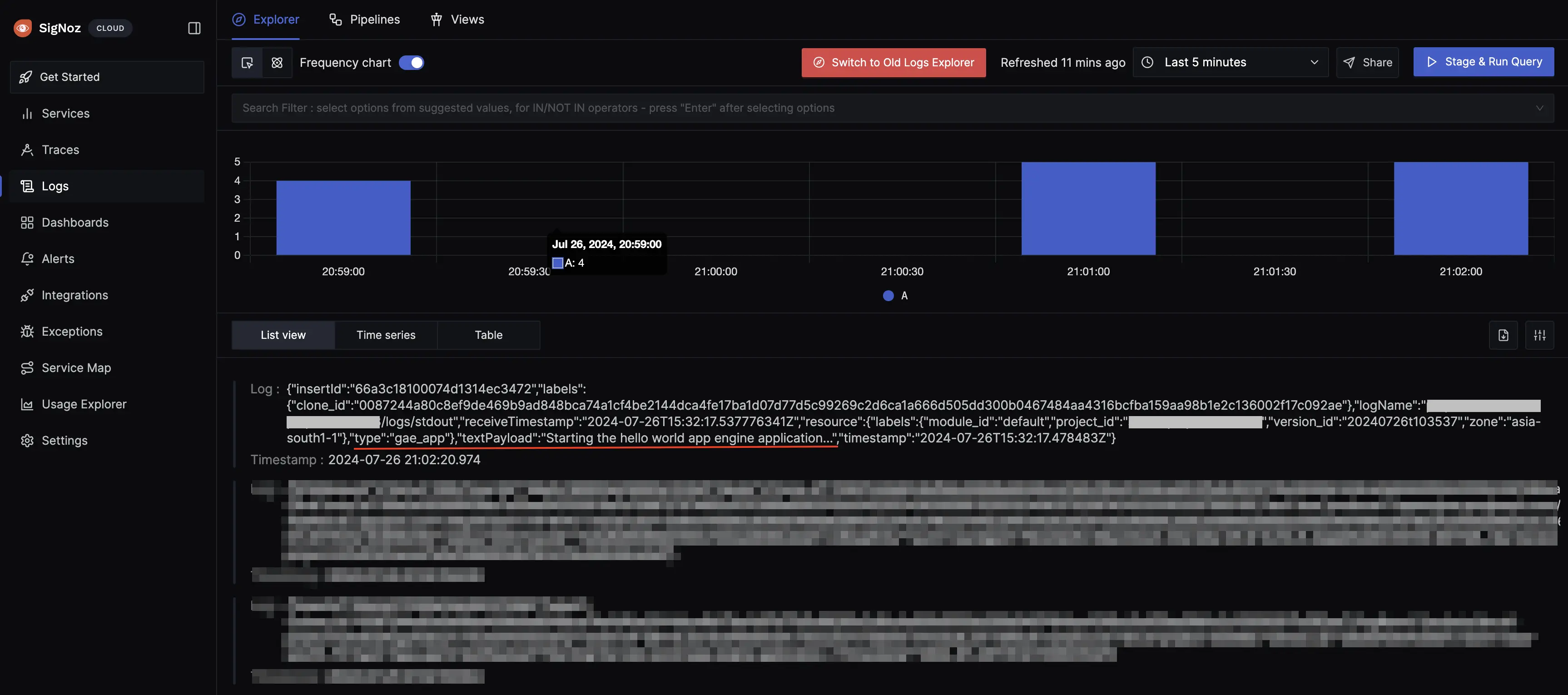
App Engine Logs in SigNoz Cloud
